Erectile Dysfunction, ED, affects most men around the world. The US alone records about 30 million cases[1]. While younger men can suffer from the condition, older men, aged 70+, are the most affected.
You can treat impotence with prescription medication. However, there are many over-the-counter (OTC) medications that might help manage this sexual dysfunction.
Take care to ascertain whether the medications actually work and are safe for use. Most dietary supplements market themselves as “natural” pills for ED. Let’s take a peek at these options and find out if they’re worth the hype.
OTC supplements for ED
Some of the dietary and herbal pills you can use to help boost sex drive include the following.
1. Performer 8
Performer 8 works in 3 ways to help you give a more satisfying performance in the bedroom every time:
- widens and clears blood vessels for harder erections
- increases semen production for a more satisfying orgasm
- elevates your sex drive so you’re always ready to go
It’s packed with 9 active ingredients, including KSM66, Barrenwort and Glucuronolactone that are backed by clinical studies to give you harder erections and reduce impotence.
Unlike drugs like Viagra, you don’t need to remember to take it half an hour before sex – which can be enough time to kill the mood. Just take it daily with food, like a regular vitamin.
This OTC ED supplement comes with a 60 day money-back guarantee and you can claim a refund if it doesn’t work for you.
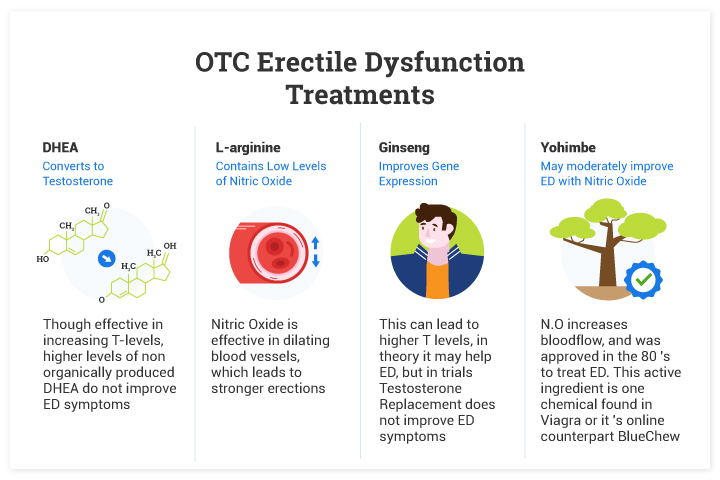
2. DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone)
This OTC supplement may be of help[2] if your ED isn’t due to diabetes or any nerve-related conditions. Although, there’s not sufficient proof to justify its effectiveness.
DHEA stimulates the production of sexual hormones in men and women. At age 30+, however, the levels of this hormone might be compromised in your body, risking[3] your chances of developing ED.
Note that you might experience the following side effects with dehydroepiandrosterone.
- Acne
- An urgency to urinate
- Issues with sleep
- Aggressiveness
- Breast tenderness
- Reduced size of the testes
DHEA is found naturally in yams (and certain soy products).
3. Viasil
This ODC drug helps bring the ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and nitric oxide levels in the body back to normal. These two chemicals produced are responsible for giving energy and ensuring that blood flows the right way.
With no recorded side effects, ingredients like Epimedium brevicornum (horny goat weed), Panax ginseng root, pomegranate, Ginkgo Biloba, Citrus Sinensis, zinc, and Tribulus Terrestris make up the Viasil drug.
Viasil gives longer and harder erections, increases libido, treats erectile dysfunction, and impotence.
4. Vigrx Plus
Manufactured by leading Edge Health, the clinical trials for this drug were carried out on humans and not lab rats to prove its potency.
This product has been proven to add at least 2 inches in length and 1 inch in girth to the penis. It also improves sexual stamina, increases testosterone level, gives bigger, harder, and lasting erections, and increases orgasms.
The major substance in Vigrx plus is Bioperine, this ingredient increases the rate at which the drug takes effect and delivers the other ingredients in the drug straight to the cells that need them.
The effect of this pill is long-lasting; this means you do not need to take the pills every time you want to have sex.
5. L-arginine

One of the popular amino acid supplements, L-arginine may help treat erection problems by improving blood flow to the penis.
It’s converted into nitric oxide, aiding your blood vessels to open wider.
Based on some experiments, you can pair[4] L-arginine with other ED medication, including yohimbine and glutamate. You can also combined it[5] with pycnogel – an extract of a tree bark.
Side effects[6] include:
- Low levels of blood sugar
- Nausea
- Mild cramping
- Raise bleeding risks when combined with certain drugs
While L-arginine has been widely used to treat[7] metabolic alkalosis in children, it’s yet to be approved as an ED treatment by FDA.
6. Ginseng

Available in pill and cream form, ginseng helps boost sexual function[8] in men. The supplement is popularly known as red ginseng, but you can also refer to it as Panax or Chinese ginseng.
According to a study[9] performed on men with mild-to-moderate ED, ginseng can help improve your overall sexual satisfaction, including orgasm and sexual desire. You should take it for up to eight weeks.
Seek medical advice before using this common herbal pill. It can interact with different medications.
Note that it can cause sleeping problems, characteristic of stimulants. If you’re suffering from heart disease, bleeding conditions, or illnesses of the auto-immune system.
Ginseng can cause adverse side effects, including headaches, diarrhoea, and nausea.
Still, more research should be done to ascertain it as a viable treatment for ED.
7. Yohimbe

A products of an African tree, Yohimbe is sold as a treatment option for erectile dysfunction. It promotes ejaculation and orgasmic function in men, according to a study[10].
Thanks to its active substance (Yohimbine), Yohimbe helps boost blood blow to the penis. It also initiates the production of norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter that aids boost erections.
You might experience anxiety, irregular heartbeats, and heightened blood pressure as a result of using of using Yohimbine. That’s why some medical experts will unlikely recommend it for you.
Note, there’s no sufficient evidence to support the effectiveness of Yohimbe in helping boost libido.
8. Propionyl-L-carnitine
Propionyl-L-carnitine is related to L-carnitine, an amino-acid derivative.
It is an ideal ED solution. It helps improve blood flow and other issues stemming from the circulatory system. Several studies[11] have concluded that both L-carnitine and propionyl-L-carnitine can help boost[12] the effects of the enhancement male pill, viagra.
Point of caution
Some OTC pills advertised for ED are a controversial lot in the medical field. While they may be labeled natural, they could contain harmful, hidden ingredients, according to the Food and Drug Administration, FDA.
OTC products that are supposed to enhance sex are not FDA regulated, either. Further, certain herbs have not been tested on humans, despite their effectiveness in treating ED in animals. They may lead to unexpected side effects.
FDA states that approximately 300[13] ED products feature unusual amounts of undisclosed ingredients. The organization has listed[14] some 29 “dietary pills” you should avoid.
Interactions
Some OTC drugs for ED could interact with other erectile dysfunction drugs. Some more may contain substances that interact with other medications you’re taking to manage other conditions.
The (OTC) medications featuring sildenafil may also interact with drugs containing nitrates, leading to a fall in blood pressure.
Consequently, if you’re treating pulmonary hypertension with traditional pills for erectile dysfunction, including the over counter Viagra pill, don’t combine them[15] with medications containing alpha-blockers and nitrates. It could be risky.
Proof
There isn’t sufficient evidence to prove that the above OTC drugs improve sexual performance. They may show little to no success.
Seek medical advice before using any of these dietary supplements – especially if you’re using supplementary medicines or are suffering from other health disorders. It doesn’t matter if the pills are marketed as “natural” or not.
OTC ED Pills vs Prescription medications
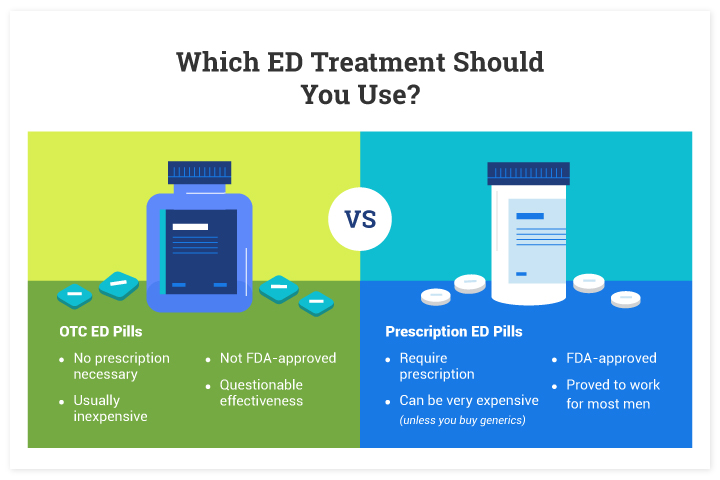
Unlike the OTC medications for erectile dysfunction, prescription medications are approved by the FDA. They are prescribed by your doctor after an examination. Here are four main oral prescription medications for ED.
- Viagra, sildenafil
- Cialis, tadalafil
- Staxyn (Levitra), vardenafil
- Stendra, avanafil
Companies like Bluechew offer sildenafil, aka generic viagra, as a monthly subscription service delivered by mail. They only require an online assessment to be completed, making them a bit of a hybrid between OTC ED supplements and more expensive prescription ED pills like Viagra.
These medications are often successful in treating erectile dysfunction. They boost the nitric oxide effects – nitric oxide is a chemical your body generates to help ease the penis muscles.
You’ll still require sexual stimulation to obtain an erection with these prescription drugs. They are PDE-5 inhibitors; they don’t function like a charm.
Note, while similar, the above drugs are administered in different dosages. They have varied potential side effects, too, as is the duration of their action.
You might experience these possible side effects.
- Stomach upsets
- Headache
- Backache
- Changes in ability to see
- Nasal congestion
A health expert can help you choose what best works best for you. Nevertheless, some ED medications can be risky. Do not use them if you’re on nitrate drugs or have the following conditions.
- Liver disease
- Heart issues
- Kidney disease
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure
Additional treatment options for ED
Apart from prescription medications and over the counter ED pills, you can manage erectile dysfunction using additional treatments.
Medical options include:
- Testosterone replacement
- Surgery of the blood vessels
- Suppository of the alprostadil urethral
- Penis injections
- Penile implants
- Vacuum pumps
Natural methods include:
Rhodiola Rosea
Rhodiola Rosea might help improve sexual energy[16], based on a study. 26 men out of 35 reported an improvement in sexual activity after being treated with this herb for three months. Nevertheless, the safety of Rhodiola Rosea isn’t yet ascertained, and the mechanism by which it works is still under research.
Zinc supplements
If your zinc levels are low, you can use zinc supplements as an alternative therapy to help boost your sex drive. The herbs ginkgo and ashwagandha are some of the options you can use. Note that these are still undergoing research to ascertain their effectiveness.
Watermelon
A study[17] shows there’s a link between impotence and watermelon. The fruit boasts citrulline, a compound that helps ease blood vessels while boosting blood flow. That’s typical of erectile dysfunction drugs.
Cocoa
According to research[18], flavonoids can improve your cardiovascular health. These compounds increase the strength of nitric oxide in the blood, which is key when it comes to developing and maintaining an erection. Dark chocolate is one of the foods rich in flavonoids.
Pick Pistachios
This green nut might help boost sexual function. A study[19] shows improved sexual performance when you consume pick pistachios for weeks. Pistachios can also help keep your blood pressure and cholesterol levels in check.
Acupuncture
Results show promising results with acupuncture as an ED treatment. One study[20] shows that acupuncture boosts the quality of erection in men. An advanced study[21] proves that acupuncture helps enhance erection. Despite all of these, acupuncture is still undergoing research when it comes to treating erectile dysfunction.
If you’re treated by acupuncture, you’re likely to experience minimum risks[22].
Healthy lifestyle habits
ED is associated with insufficient blood flow to the penis. Consequently, examine your lifestyle – some habits can compromise blood flow in your body, increasing impotence chances.
Healthy lifestyle habits that can help prevent ED include exercising frequently and avoiding cigarettes and liquor. You should maintain healthy weight and low blood pressure, too.
Keeping your blood vessels in good shape by eating a healthy diet is likely to lower your chances of being impotent, too. Based on a study, men who eat healthy food consistently are unlikely to experience erectile dysfunction.
Healthy food helps keep your triglyceride, blood sugar, and cholesterol levels in check. It also limits your risks of being overweight.
The Take-Away
While erectile dysfunction affects most men, the condition can be treated. For diagnosis or treatment, ensure you consult a qualified medic. They can help find an option (or combination of options) that works best for you.
If you prefer natural options, rely on those that are backed by research. Most herbal options might not be a good fit for you; there’s little evidence supporting their effectiveness. Most of them are not regulated, either.
Sources:
[1] – https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/erectile-dysfunction/definition-facts
[2] – https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/natural/331.html
[3] – https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(17)34871-1
[4] – https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0302283802001756
[5] – https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00926230390155104
[6] – https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements-l-arginine/art-20364681
[7] – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5916438/
[8] – https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03236.x
[9] – https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2012.45
[10] – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3731873/
[11] – https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0090429505006515
[12] – https://www.nature.com/articles/s41443-018-0036-4
[13] – https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/all-natural-alternatives-erectile-dysfunction-risky-proposition
[14] – https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/hidden-risks-erectile-dysfunction-treatments-sold-online
[15] – https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.944603
[16] – http://cms.herbalgram.org/herbalgram/issue56/article2333.html?ts=1492616880&signature=6fa2087cf82b321d6a5223f04195653e
[17] – https://today.agrilife.org/2008/06/30/watermelon-may-have-viagra-effect-secrets-of-phyto-nutrients-are-being-unraveled/
[18] – https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/circulationaha.108.827022
[19] – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21228801
[20] – http://www.nature.com/ijir/journal/v11/n1/abs/3900381a.html
[21] – http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14562135
[22] – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25052025